Note
Click here to download the full example code
Array Beamforming
This example uses the frequency domain lyceanem.models.frequency_domain.calculate_farfield() function to predict
the farfield patterns for a linearly polarised aperture with multiple elements. This is then beamformed to all farfield points using multiple open loop beamforming algorithms to attemp to ‘map’ out the acheivable beamforming for the antenna array using lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming.MaximumDirectivityMap().
The Steering Efficiency can then be evaluated using lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming.Steering_Efficiency() for the resultant achieved beamforming.
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import copy
Setting Farfield Resolution and Wavelength
LyceanEM uses Elevation and Azimuth to record spherical coordinates, ranging from -180 to 180 degrees in azimuth, and from -90 to 90 degrees in elevation. In order to launch the aperture projection function, the resolution in both azimuth and elevation is requried. In order to ensure a fast example, 37 points have been used here for both, giving a total of 1369 farfield points.
The wavelength of interest is also an important variable for antenna array analysis, so we set it now for 10GHz, an X band aperture.
az_res = 181
elev_res = 37
wavelength = 3e8 / 10e9
Geometries
In order to make things easy to start, an example geometry has been included within LyceanEM for a UAV, and the
open3d.geometry.TriangleMesh structures can be accessed by importing the data subpackage
import lyceanem.tests.reflectordata as data
body, array, source_coords = data.exampleUAV(10e9)
Visualise the Resultant UAV and Array
open3d.visualization.draw_geometries() can be used to visualise the open3d data
structures open3d.geometry.PointCloud and open3d.geometry.PointCloud
mesh_frame = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_coordinate_frame(
size=0.5, origin=[0, 0, 0]
)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([body, array, source_coords, mesh_frame])
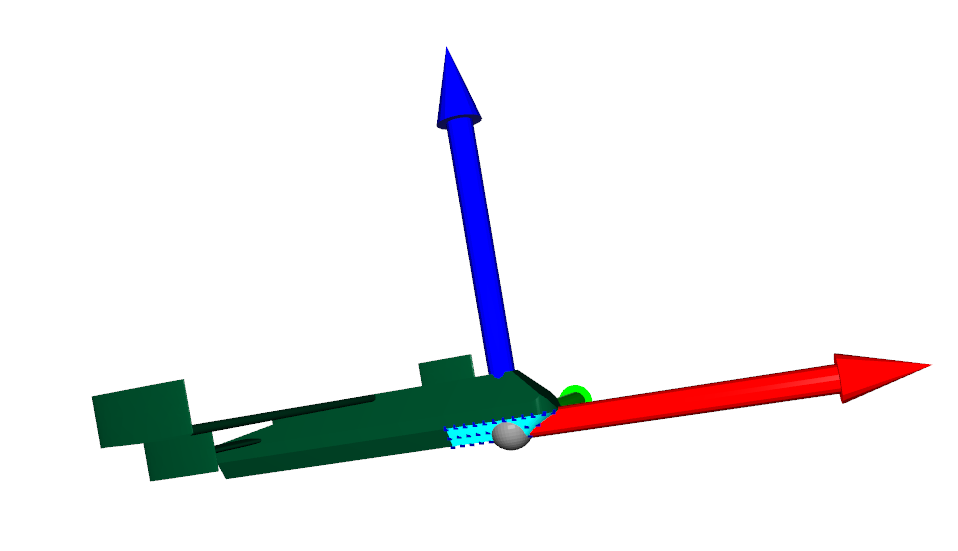
from lyceanem.base_classes import points,structures,antenna_structures
aperture=points([source_coords])
blockers = structures([body, array])
uav_structure=antenna_structures(blockers, aperture)
#put rotations here
surface_array = copy.deepcopy(array)
surface_array.triangles = o3d.utility.Vector3iVector(
np.asarray(array.triangles)[: len(array.triangles) // 2, :]
)
surface_array.triangle_normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(
np.asarray(array.triangle_normals)[: len(array.triangle_normals) // 2, :]
)
array_surface_area=surface_array.get_surface_area()
maximum_aperture_efficiency=(4*np.pi*array_surface_area)/(wavelength**2)
Model Farfield Array Patterns
The same function is used to predict the farfield pattern of each element in the array, but the variable ‘elements’
is set as True, instructing the function to return the antenna patterns as 3D arrays arranged with axes element,
elevation points, and azimuth points. These can then be beamformed using the desired beamforming algorithm. LyceanEM
currently includes two open loop algorithms for phase weights lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming.EGCWeights(),
and lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming.WavefrontWeights()
from lyceanem.models.frequency_domain import calculate_farfield
desired_E_axis = np.zeros((1, 3), dtype=np.float32)
desired_E_axis[0, 2] = 1.0
Etheta, Ephi = calculate_farfield(
source_coords,
blockers,
uav_structure.excitation_function(desired_e_vector=desired_E_axis,point_index=[0]),
az_range=np.linspace(-180, 180, az_res),
el_range=np.linspace(-90, 90, elev_res),
wavelength=wavelength,
farfield_distance=20,
elements=True,
project_vectors=False,
)
from lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming import MaximumDirectivityMap,MaximumDirectivityMapDiscrete
az_range = np.linspace(-180, 180, az_res)
el_range = np.linspace(-90, 90, elev_res)
directivity_map_discrete = MaximumDirectivityMapDiscrete(
Etheta, Ephi, source_coords, wavelength, az_range, el_range, phase_resolution=np.array([2,4,6,8],dtype=int)
)
from lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming import PatternPlot
az_mesh, elev_mesh = np.meshgrid(az_range, el_range)
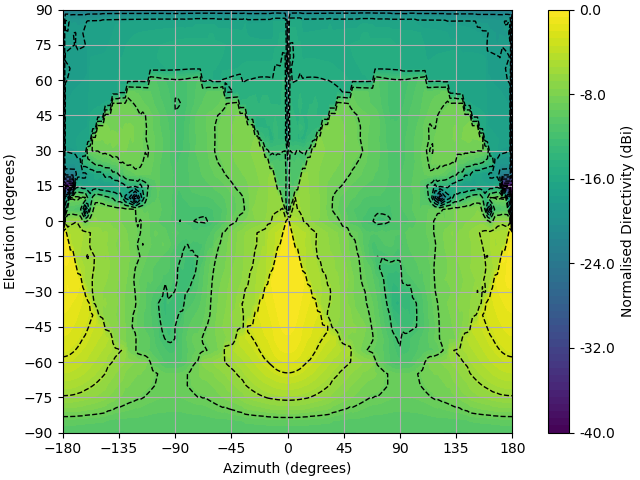
PatternPlot(
directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 2,3], az_mesh, elev_mesh, logtype="power", plottype="Contour"
)
C:\Users\lycea\anaconda3\envs\cusignal-dev\lib\site-packages\numba\cuda\cudadrv\devicearray.py:885: NumbaPerformanceWarning: Host array used in CUDA kernel will incur copy overhead to/from device.
warn(NumbaPerformanceWarning(msg))
C:\Users\lycea\PycharmProjects\LyceanEM-Python\lyceanem\electromagnetics\beamforming.py:1167: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
logdata = 10 * np.log10(data)
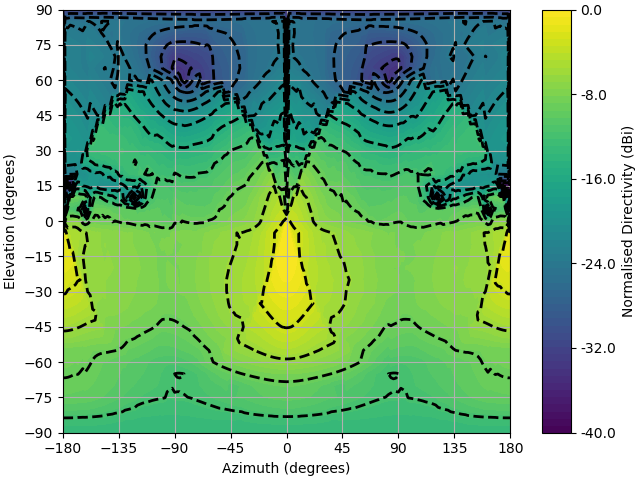
from lyceanem.electromagnetics.beamforming import Steering_Efficiency
for inc in range(4):
setheta, sephi, setot = Steering_Efficiency(
directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 0,inc],
directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 1,inc],
directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 2,inc],
np.radians(np.diff(el_range)[0]),
np.radians(np.diff(az_range)[0]),
4 * np.pi,
)
print("Steering Effciency of {:3.1f}%".format(setot))
#print("Steering Effciency Product of {:3.1f}%".format(setot*np.max(directivity_map_discrete[:,:,2,inc]/maximum_aperture_efficiency)))
print("Steering Effciency Product of {:3.1f}%".format(np.max(directivity_map_discrete[:,:,2,inc])/maximum_aperture_efficiency))
print(
"Maximum Directivity of {:3.1f} dBi".format(
np.max(10 * np.log10(directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 2,0]))
)
)
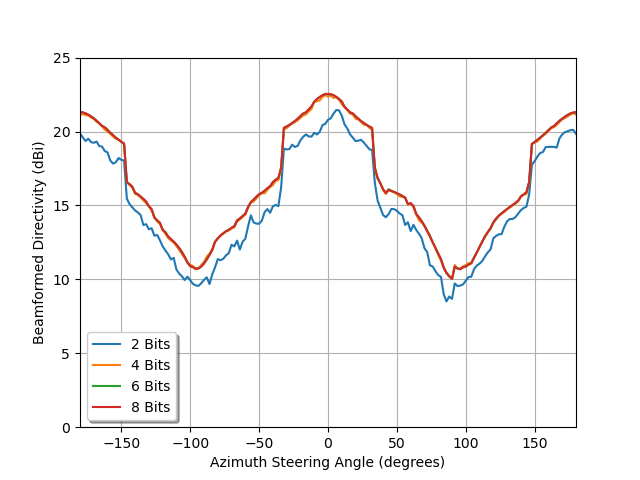
comparison=directivity_map_discrete[9,:,2,:]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig,ax=plt.subplots()
ax.plot(az_range,10*np.log10(comparison[:,0]),label='2 Bits')
ax.plot(az_range,10*np.log10(comparison[:,1]),label='4 Bits')
ax.plot(az_range,10*np.log10(comparison[:,2]),label='6 Bits')
ax.plot(az_range,10*np.log10(comparison[:,3]),label='8 Bits')
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_xlim(-180,180)
ax.set_ylim(0,25)
ax.set_ylabel('Beamformed Directivity (dBi)')
ax.set_xlabel('Azimuth Steering Angle (degrees)')
legend = ax.legend(loc='lower left', shadow=True)
Steering Effciency of 9.3%
Steering Effciency Product of 1.1%
Steering Effciency of 8.9%
Steering Effciency Product of 1.5%
Steering Effciency of 9.0%
Steering Effciency Product of 1.5%
Steering Effciency of 9.1%
Steering Effciency Product of 1.5%
C:\Users\lycea\PycharmProjects\LyceanEM-Python\docs\examples\08_beamforming_architecture.py:137: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
np.max(10 * np.log10(directivity_map_discrete[:, :, 2,0]))
Maximum Directivity of 21.6 dBi
Total running time of the script: ( 8 minutes 23.069 seconds)